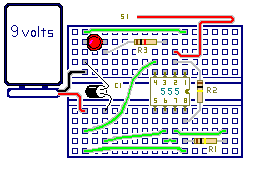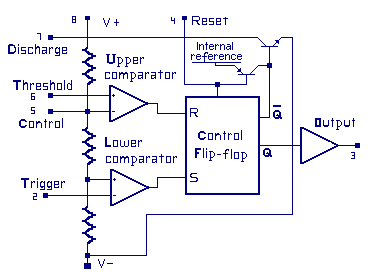
Introduction
Chapter 1 - Electricity
Chapter 1.2 - The Numbers
Chapter 2 – Sharing and Bonding
Chapter 3 - Voltage
Chapter 3.2 – Voltage Static
Chapter 3.3 - Batteries
Chapter 3.4 – Solar - Others
Chapter 4 - Resistance
Chapter 4.2 – Parallel Resistance
Chapter 4.3 – Voltage Dividers
Chapter 5 - Semiconductor
Chapter 5.2 - PNP NPN Junctions
Chapter 6 – AC and Hertz
Chapter 7 - Magnetism
Chapter 7.2 - Inductors
Chapter 8 - Capacitor
Chapter 9 - IC's and OP-AMP's
Chapter 9.2 - Feedback, Unity Gain
Chapter 9.3 - Non-inverting Amplifier
Chapter 9.4 - Inverting Amplifier
Chapter 10 - 555 Timer
Chapter 10.2 - 555 Timer- Part 2
Chapter 11 - Logic
Chapter 12 - The Power Supply
Chapter 12.2 - More on Power Supplies
|
|
Copyright 2007-2012, All Right Reserved
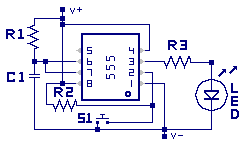 This configuration of the 555 is called a ONE-SHOT Mulivibrator. The name comes from
the circuit configuration allowing one action after the trigger. Once triggered, the
output will stay in the triggered state for a period of time based on the RC time
interval. Then switch back to the wait state and wait until another
trigger is sent. NOTE: As we move on in the study other oscillator circuits using
different components will also be referred to as a ONE-SHOT Mulivibrator.
This configuration of the 555 is called a ONE-SHOT Mulivibrator. The name comes from
the circuit configuration allowing one action after the trigger. Once triggered, the
output will stay in the triggered state for a period of time based on the RC time
interval. Then switch back to the wait state and wait until another
trigger is sent. NOTE: As we move on in the study other oscillator circuits using
different components will also be referred to as a ONE-SHOT Mulivibrator.